
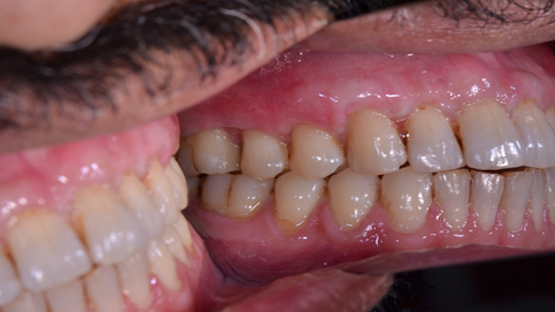
Gum grafting is a procedure in which the gum tissue around a tooth pulls away from the tooth, exposing more of the tooth or its base. The supporting bone may be harmed as a result of this. Gum recession is a common dental issue that affects 4% to 12% of adults and sometimes goes undiscovered until it becomes more serious.
What Happens During a Gum Tissue Graft Procedure?
Gum tissue transplants are usually performed in three basic ways. Your dentist will utilise whichever type is best for you based on your individual circumstances. The following are some of the transplant procedures:
Connective-tissue grafts: This is the most popular technique of root exposure treatment. A flap of skin is cut at the roof of your mouth (palate), and tissue from beneath the flap, known as subepithelial connective tissue, is taken and sewn to the gum tissue surrounding the exposed root during the treatment.
Free gingival grafts: Free gingival grafts are similar to connective-tissue grafts in that they employ tissue from the roof of the mouth. Instead than generating a flap and removing tissue beneath the top layer of flesh, a little amount of tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth and linked to the gum area that is being treated.
Pedicle grafts: Instead of removing tissue from the palate, it is transplanted from the gum around or near the tooth that needs to be repaired in this surgery. The flap, referred to as a pedicle, is only partially sliced away, leaving one edge intact. After that, the gum is pushed over or down to cover the exposed root and sewed in place. This technique is only possible for patients who have a lot of gum tissue around their teet
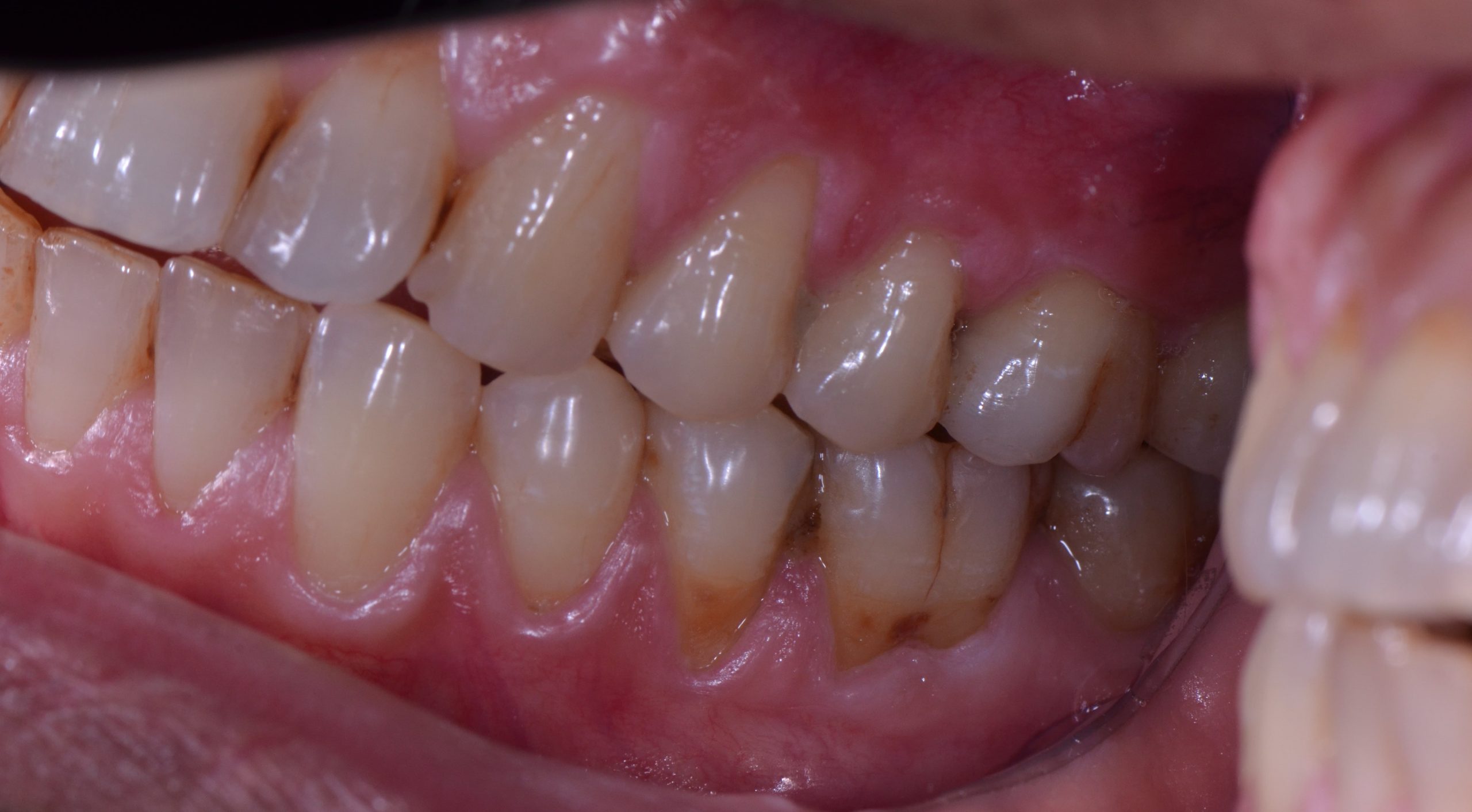
GUM GRAFTING
Your smile is one of the first things people notice about you. If you’re embarrassed by receding gums or experience discomfort due to increased sensitivity, you might hide your mouth behind your hand or refuse to grin at all. Traditional gum recession treatment, while effective, involves a painful procedure with a lengthy recovery process. Patients hesitant to undergo surgical gum grafting have had limited options for restoring a healthy smile—until now.
At San Diego Periodontics & Implant Dentistry, we’re proud to offer our patients a scalpel-free and suture-free restorative gum recession treatment that provides instant cosmetic improvement with minimal downtime.
What causes gum recession?
Research shows that 88% of individuals over the age of 65 have receding gums in at least one tooth. Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is a loss of gum tissue that exposes the roots of the teeth. When these fragile roots are introduced to bacteria, plaque, and decay, patients may experience tooth sensitivity, pain, or infection. Cosmetically, receding gums makes the teeth appear longer and create the illusion of black triangles where the tooth meets the gum.
Gum recession is often caused by poor oral hygiene and periodontal disease, but receding gums can happen to people who regularly visit the dentist, too. Some have a genetic predisposition for receding gums due to tooth position and gum thickness. Others who vigorously brush their teeth or use a hard bristled toothbrush may physically wear down the gums and cause gum recession. Lip piercings, smoking and using other tobacco products, misaligned teeth, and damage caused by dental treatment are also common culprits.
Gum Recession Treatment with Soft Tissue Grafting
Soft tissue graft treatment is a long-term way to treat gum recession, allowing you to immediately identify and resolve your periodontal issues. Soft tissue grafting involves taking healthy tissue from elsewhere in the mouth and using it to treat the receding gums, covering the exposed tooth roots.
What Are the Different Types of Soft Tissue Grafts?
Different techniques exist to regenerate lost gum tissue. Some techniques use your own gum tissue (autograft) and other techniques may involve donor tissue, either originating from a cadaver source (allograft) or animal source (xenograft). Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages; it just depends on your individual case and what you and the periodontist are trying to achieve.
Normal gum tissue is typically composed of two layers: an outer “epithelial” layer and an inner “connective tissue” layer.
In a free gingival graft, a small piece of tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth and attached to the recession site to encourage natural growth. This involves the removal of both the outer and inner layer of gum tissue to be removed. This technique is used if there is a recession area that needs to be reinforced or thickened with strong gum tissue. Typically, a second procedure may be necessary to move the gum tissue up to cover the roots. Color matching of the gum tissue is not ideal and there may be more postoperative discomfort.
The connective tissue graft is the most common type soft tissue autograft. A small inner layer of connective tissue is removed, typically from the roof of the mouth, and is then placed onto the recession area to attach and cover the exposed tooth roots. This method is more esthetic as it blends to the surrounding gum tissue and is less invasive than the free gingival graft. It can help resolve areas of sensitivity caused by recession.
The advantage of using allograft or xenografts is that you don’t have to get gum tissue from your own mouth. Allografts do not limit how many recession areas can be treated at one time compared to an autograft so that a whole arch or whole mouth can be all completed in one visit. However, we must note that it does not work in all cases.
Some techniques that use this type of graft are the Edward Allen Tunneling Technique, the Chao Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation Technique, and the VISTA technique. All of these techniques are minimally invasive as they utilize minimal incisions to access and peel the gum tissue from the underlying bone, compared to the larger traditional flap access. Because it is less invasive, there is also less postoperative discomfort.
We will send you a confirmation within 48 hours. For more information, Call: +92 300 268 5875
Call us today for a consultation to enable you to make a considered and informed choice about your dental care.